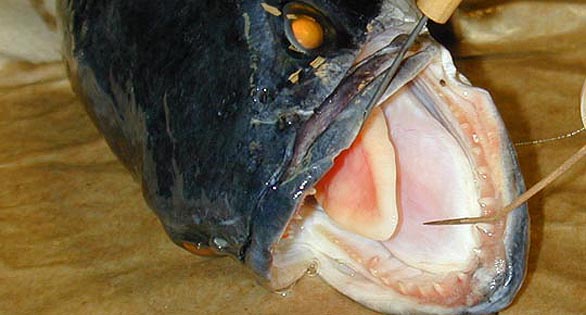
A large, fearsome predator, the Northern Snakehead grows to lengths in excess of 40 in (1 m) and has a notorious worldwide reputation as an invasive species. Credit: Maryland Dept. of Fisheries Service.
Peaceful Harlem Meer has long been a place to cast a fly or a worm-baited hook in hopes of catching something in the panfish category—yellow perch, small bass, and crappies—but several fishermen have been reporting surprise or downright terror when they have latched into toothy gamefish with pugnacious attitudes and mouthsfull of razor-sharp teeth.
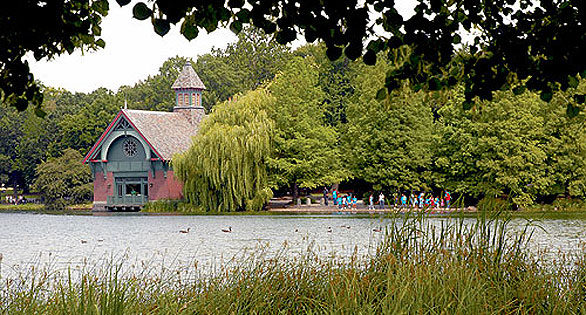
Harlem Meer, a manmade lake dating from the 1860s in New York’s Central Park, is now reported to be home to a population of introduced Northern Snakeheads, Channa argus. Credit: Central Park Conservancy.
Tucked into the northeastern corner of New York City’s Central Park, Harlem Meer is an 11-acre manmade body of water created started in 1861 today appears to have been invaded by Northern Snakeheads, Channa argus, an apex freshwater predator native to China and Korea and a notorious introduced species in a number of countries and U.S. states, including Florida, Maryland, California, Pennsylvania, and elsewhere, including British Columbia in Canada.
There is considerable concern among North American fish and wildlife experts that the Northern Snakehead might make it into the Great Lakes and seriously disrupt a huge aquatic ecosystem. NY officials say it is “unlikely” it can migrate from Central Park and end up in the Hudson River, and thence spread northward to Lake Champlain, the St. Lawrence River and westward toward Lake Ontario.
Biologists regard this fish, which can grow to lengths in excess of 40 inches (102 cm) and more than 15 pounds (6.8 kg), as a voracious species capable of seriously impacting native species of fishes and other aquatic life. Dubbed “Fishzilla” or “Frankenfish” by some, it has the anatomical ability to breathe aerially, making it capable of living out of water for several days. Young of the species are reported to be able to wriggle overland for short distances, raising the spectre of the fish migrating from one body of water to another.
Intentional Releases
Although aquarists are often blamed for releasing exotic fishes into the wild, most of the blame regarding snakeheads is pointed at the Asian food fish trade, which traditionally offers live snakeheads for sale to cooks. Federal US law has forbid the possession, sale, or transport of live snakeheads since 2002, but they are in high demand for Asian cookery and folk medicine uses and somehow make their way into North American markets.

Northern Snakehead is prized by Asian chefs for its first flesh, but represents the sort of new predator that could dominate ecosystems where it is artificially introduced. Credit: USGS.
In a recent article on the newly discovered Harlem Meer population, Marc Santora of The New York Times reported one potential major source of the species in the New York area:
“After the seizure of 353 live snakeheads at Kennedy International Airport on the eve of the 2010 Chinese New Year, an investigation led to the arrest of a local wholesaler in 2011 who illegally imported thousands of snakeheads and sold them from a shop in Brooklyn.”
Authorities are trying to determine the extent of population of the Central Park snakeheads and have not yet announced any control measures. In other instances, snakeheads have been exterminated by the use of the botanical rotenone, which unfortunately wipes out all other fishes in the same body of water.
Fish and wildlife managers are telling fishermen that hooked snakeheads must never be released, but rather turn in to authorities or killed by “cutting or bleeding.” A wooden stake through the heart is said to be effective.
Further reading:
Recommended: Read full New York Times article.
USDA National Invasive Species Information Center: Northern Snakehead





